2.3.1 Measurements
are to be made to the surface of the parent plate and not to a weld,
fitting or other raised part.
2.3.2 In assessing
the out-of-roundness of pressure vessels, the difference between the
maximum and minimum internal diameters measured at one cross-section
is not to exceed the amount given in Table 4.2.1 Tolerances for cylindrical
shells.
Table 4.2.1 Tolerances for cylindrical
shells
| Nominal internal diameter of
vessel, in mm
|
Difference between maximum and
minimum diameters
|
Maximum departure from designed
form
|
- ≤ 300
- > 300 ≤ 460
- > 460 ≤ 600
- > 600 ≤ 900
- > 900 ≤ 1220
- > 1220 ≤ 1520
- > 1520 ≤ 1900
|
1,0 per cent of
internal diameter
|
- 1,2 mm
- 1,6 mm
- 2,4 mm
- 3,2 mm
- 4,0 mm
- 4,8 mm
- 5,6 mm
|
- > 1900 ≤ 2300
- > 2300 ≤ 2670
- > 2670 ≤ 3950
|
19 mm
|
|
|
|
19 mm
0,4 per cent of internal diameter
|
0,2 per cent of
internal diameter
|
2.3.4 Shell
sections are to be measured for out-of-roundness, either when laid
flat on their sides or when set up on end. When the shell sections
are checked while lying on their sides, each measurement for diameter
is to be repeated after turning the shell through 90° about its
longitudinal axis. The two measurements for each diameter are to be
averaged, and the amount of out-of-roundness calculated from the average
values so determined.
2.3.6 The
external circumference of the completed shell is not to depart from
the calculated circumference (based upon nominal inside diameter and
the actual plate thickness) by more than the amounts given in Table 4.2.2 Circumferential tolerances.
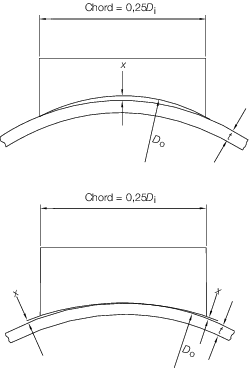
Figure 4.2.1 Tolerances for cylindrical shells
Table 4.2.2 Circumferential tolerances
Outside diameter
(nominal inside diameter plus twice actual plate thickness), in mm
|
Circumferential
tolerance
|
| 300 to 600 inclusive
|
±5 mm
|
| Greater than 600
|
±0,25 per cent
|