2.2.1 A bulkhead which includes the damper should
be constructed in accordance with 2.1.1 of
the recommendation and should be insulated to class A-60 on the stiffened
face, which should be the face which is not exposed to the heating
conditions of the test. A deck which includes the damper should be
constructed in accordance with 2.2.1 of
the recommendation and should be insulated to class A-60 on the stiffened
face, which should be the face which is exposed to the heating conditions
of the test.
2.2.2 Fire dampers should be incorporated into
or fixed to coamings or spigots, which should be welded or bolted
into the structural core. The coaming or spigot including the damper
should have a length of 900 mm (450 mm on each side of the structural
core) and a thickness as follows:
|
Widthfootnote or diameter of the duct
|
Minimum thickness of coaming or spigot
|
| Up to
and including 300 mm
|
3
mm
|
| 760
mm and over
|
5
mm
|
For widths or diameters of ducts in excess of 300 mm but
less than 760 mm, the thickness of the coaming or spigot should be
obtained by interpolation.
The coaming or spigot should be insulated as shown in Figure A1.
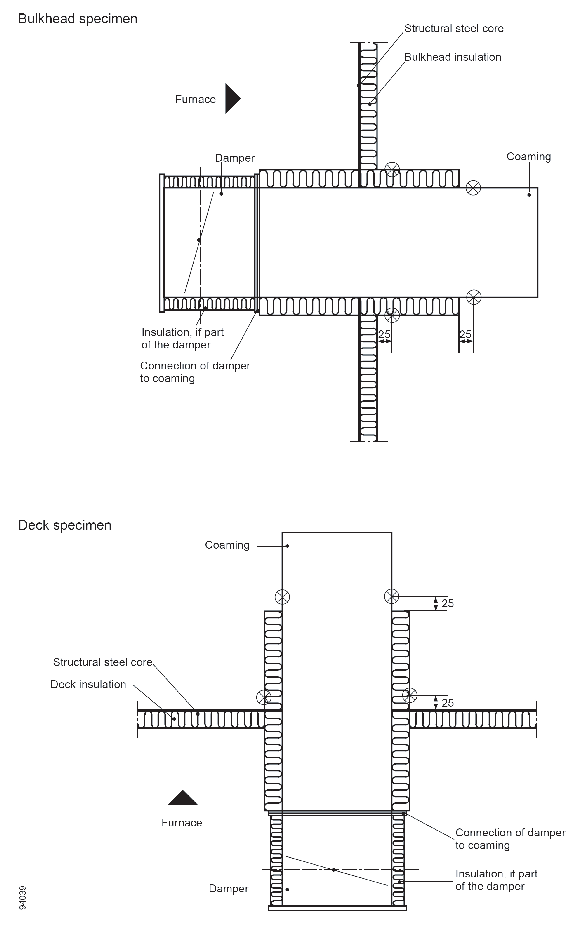
Figure A1 Fire dampers: insulation on test specimens and position of
unexposed-face - thermocouples
2.2.3 The coamings or spigots (including insulation)
should be positioned only in the top half of a bulkhead but should
be no closer than 200 mm from the edges of a bulkhead or a deck. Where
more than one damper is to be tested simultaneously in a division,
the separation between adjacent coamings or spigots (including insulation)
should not be less than 200 mm. When more than one damper is included
in a bulkhead, the top edges of all dampers should be, as far as possible,
at the same height.
2.2.4 The fire dampers should be positioned on
the exposed face of the bulkhead or deck, at a distance of at least
225 mm from the structural core, with their operative controls also
on that side of the division.
2.2.5 Fire dampers which are operated automatically
should be in the open position at the start of the test.